TMS-Cobot: Setting a new Standard for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation with Collaborative Robotics
Axilum Robotics TMS-Cobot is intended to control the positioning, the orientation and the contact of a compatible TMS coil under the supervision of an optical tracking system (no MRI) or a compatible neuronavigation system (MRI).
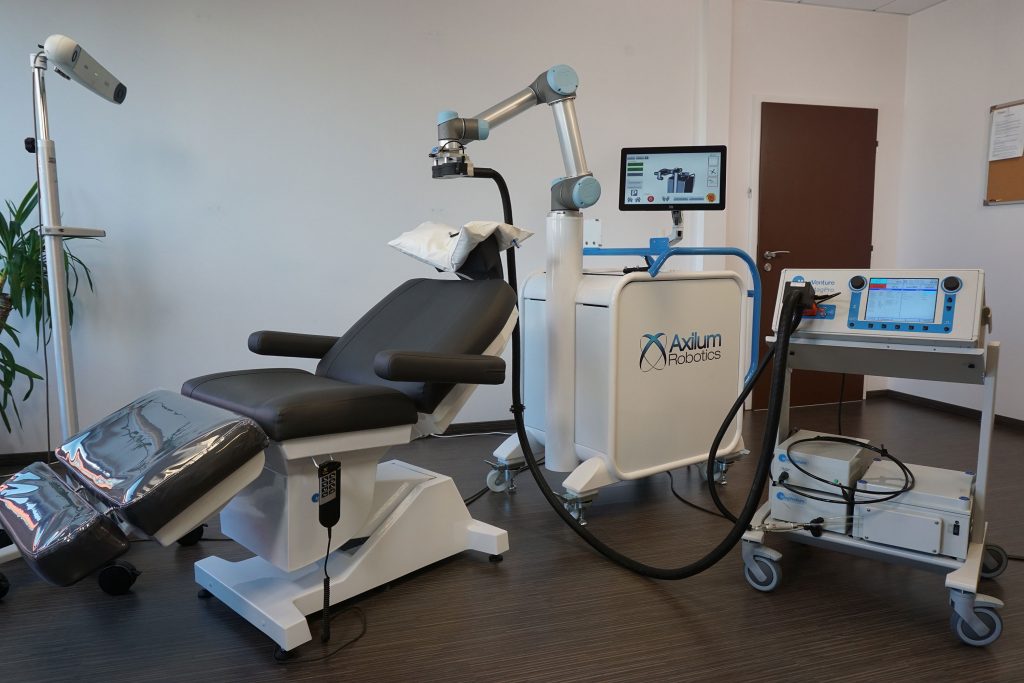 |
|||
| Optical Tracking System or compatible Neuronavigator |
Treatment chair | Axilum Robotics TMS-Cobot | Compatible Coil and Stimulator |
Why TMS-Cobot?
There is growing awareness regarding the limitations of manual TMS coil positioning. Holding the coil manually for sessions exceeding 30 minutes—or using a passive holder that forces the patient to remain perfectly rigid—leads to suboptimal outcomes. This issue is particularly critical when neuronavigation is used for MRI guidance, where precision is paramount.
Furthermore, asking a patient to avoid any head motion for 30 minutes creates significant physical constraint and discomfort.
With the increasing volume of patients, there is also a critical need to relieve the operator from this demanding, repetitive task, allowing them to focus on high-value patient care.
Our objective with the TMS-Cobot is to provide an affordable robotic solution featuring real-time head motion compensation. By automating the procedure, the TMS-Cobot significantly improves precision, reduces patient constraints, and optimizes operator workflow. Ultimately, it ensures that the stimulation dose is delivered to the exact target location every time.
Evaluating the impact of suboptimal coil positionning
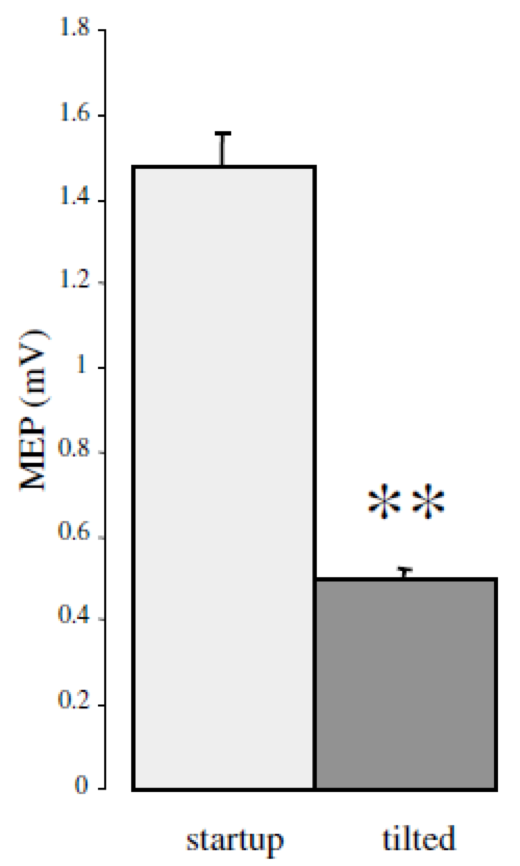
Coil rotation impact |
Coil positioning techniques impact |
 |
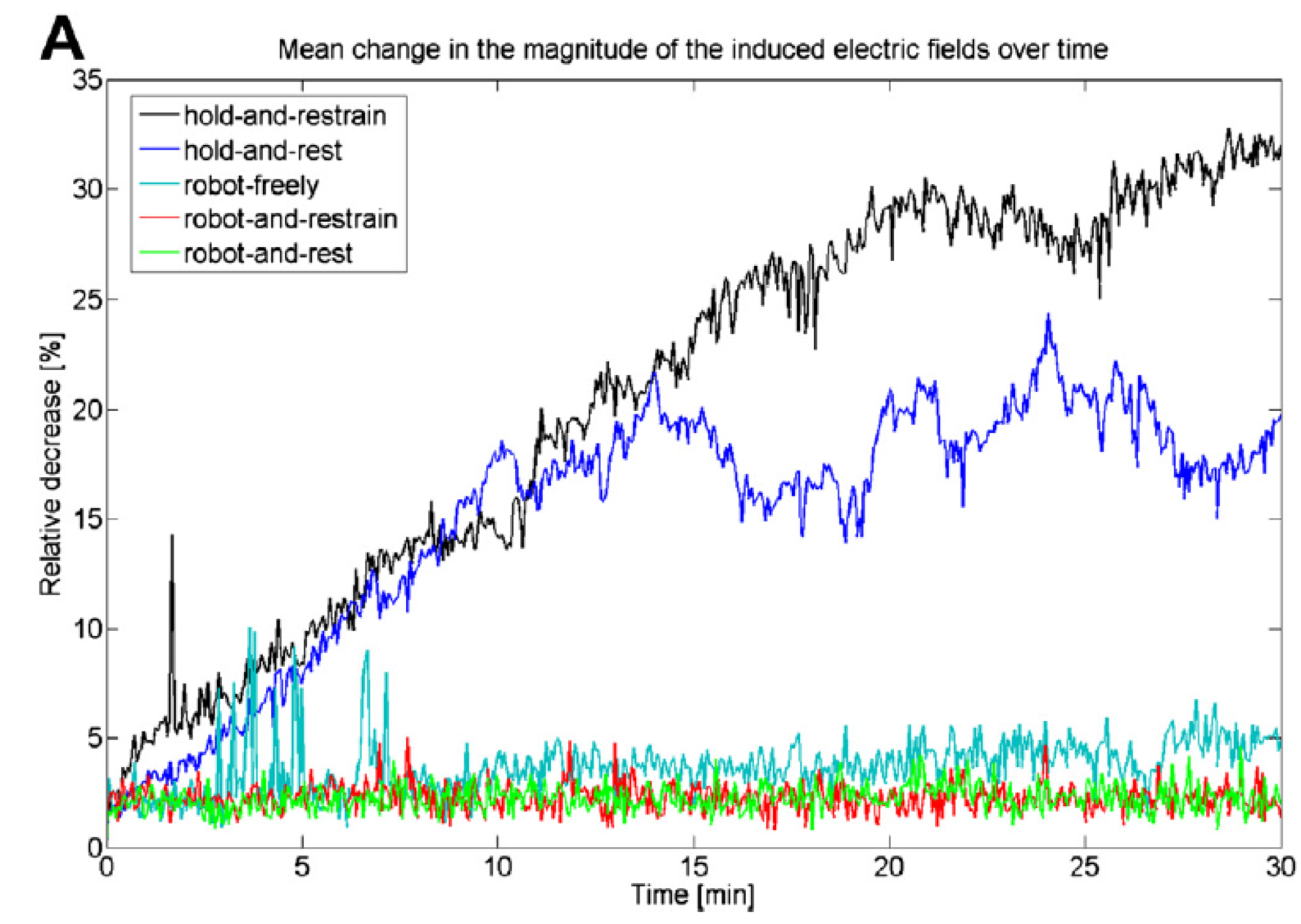 |
| Toschi et al. (1) have demonstrated the significant clinical impact of small rotations in coil position (i.e. 7°), with variation of 25% or more of the stimulus intensity and MEP drop by 60% | Richter et al. (2) have shown that with a passive holder, the induced electric field can decrease by 30% over a 30 mn period (coil holder and avoiding head motion) and still 20% when using a head rest, while robotic motion compensation results in clinically acceptable positioning throughout treatment |
Key features
- Collaborative robotics “cobot” technology (safety)
Such technology provides intrinsic safety features through a collision detection mechanism at each joint level, allowing close collaboration with human beings. Movements of the robotic arm can be either automated or manually directed by the user having activated a so-called free-drive mode - Keeps the position and the orientation of the TMS coil during the session (optical tracking of markers on the head)
- Compensates for potential head motion during the TMS session
- Ensures permanent contact between coil and head (integrated pressure sensor)
- Compatible with any chair
- Lightweight and highly mobil : Can easily be moved on its wheels.
- Ergonomy: When piloted by a compatible neuronavigation system, the operator controls TMS-Cobot from the graphical user interface of the neuronavigator. Or, when piloted by Axilum Robotics optical Tracking System, the operator controls TMS-Cobot from a control panel placed on the cart.
Key advantages
- Improves accuracy and repeatability
Accuracy of the robotic arm is below 2 mm. - Delivers the operator from a repetitive, painful and and time consuming task
Once the session launched, minimal attention of the operator is requested to ensure appropriate position, orientation and contact of the coil on the head.
Compatibility
- TMS-Cobot is compatible with coils from Deymed, Magstim, MagVenture, Mag&More, Neurosoft. List of compatible coils on request
- TMS-Cobot can be piloted either by Axilum Robotics optical Tracking System (without MRI) or compatible neuro-navigation system from Localite, Rogue Research/Brainsight, Syneika
Dimensions and Weight
TMS-Cobot fits to any space and enters into most elevators thanks to its practical dimensions and light weight.
- Height with arm : (H) 1770 mm
- Base dimensions : (L x W)1111 x 650 mm
- Weight : 143 kg
Regulatory information
- CE Mark (EU)
TMS-Cobot is a class IIa medical device, intended to automate and improve the accuracy and the repeatability of the positioning of a Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) coil, in the clinical situations where compatible devices are intended to be used, with the exception of peripheral nerve stimulation. It bears the CE marking 1639 whose conformity assessment has been established by the notified body SGS. Please read the user manual before any use. Note that these medical devices are not reimbursed by French health insurance.
- FDA 510(k) clearance (USA)
Axilum Robotics TMS-Cobot® TS MV is indicated for the spatial positioning and orientation of the treatment coil of the MagVenture TMS Therapy system (FDA clearance K182768 Class II).
Comparison between TMS-Cobot and TMS-Robot
 |
 |
|
Features |
TMS-Robot |
TMS-Cobot |
Compatible stimulator and coil |
✓ | ✓ |
Piloted by compatible neuronavigation system |
✓ | ✓ (option 1) |
Piloted by tracking system (No MRI) |
✘ | ✓ (option 2) |
Patient seat |
✓ Included, with electric adjustment | ✘ Compatible with any treatment chair |
Coil guidance |
Robotized | Robotized + manual pre-positionning |
Working space |
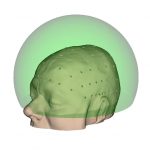 Hemi-spherical |
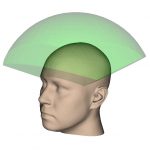 ½ Hemi-spherical |
Head motion tracking |
✓ | ✓ |
Coil contact sensor |
✓ | ✓ |
Safety |
✓ (by design) |
✓ (collaborative robot) |
Accuracy |
1 mm (ref space of NN) | < 2 mm (arm accuracy) |
Repeatability |
0,1 mm | < 2 mm |
Regulatory status |
For medical or scientific investigation purposes only Non FDA cleared |
CE mark – class IIa FDA cleared |
References
(1) Toschi N. et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in heterogeneous brain tissue: clinical impact on focality, reproducibility and true sham stimulation. J Psychiatr Res. 2009 Jan;43(3):255-64.
(2) Richter L et al. Stimulus intensity for hand held and robotic transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2013 May;6(3):315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jun 21.
